Concept of Hybridisation and its Applications
Concept of Hybridisation and its Applications: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Hybridisation, sp2 Hybridisation, sp Hybridisation, sp3d Hybridisation, dsp2 Hybridisation, sp3 Hybridisation, sp3d3 Hybridisation, Effect of Hybridisation on Bond Angle and, Rules for Hybridisation
Important Questions on Concept of Hybridisation and its Applications
In which of the following species, the underlined carbon atom is hybridised?
Which is the following has the regular tetrahedral structure?
The state of hybridisation of boron and oxygen atoms in boric acid molecule are respectively –
Which of the following is not isostructural with
Which of the following compounds is hybridised?
In which of the following species, the central atom has the maximum number of lone pair of electrons ?
Among the following transformations, the hybridisation of the central atom remains unchanged in
The hybridisations of and shown in the following compound
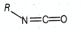
respectively, are
The hybridisation of xenon atom in is
The hybridization of in and , respectively is
The hybridization of in is
Hybridization involved in is
Hybridisation of both 'c' in acetylene molecule
In acetylene molecule, there are
Hybridisation of and of 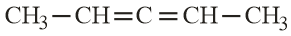 are :-
are :-
The bond angles formed by different hybrid orbitals are in the order:
Which of the following is the correct order regarding the electronegativity of hybrid orbitals of carbon?
In an octahedral structure, the pair of d-orbitals involved in hybridisation is
Assertion. molecule is planar but is pyramidal.
Reason. atom is smaller than
Assertion. is planar while is pyramidal.
Reason. in has and in has hybridization.
